Cloud Bigtable is a petabyte-scale, fully managed NoSQL database service in GCP for large analytical and operational workloads. It supports the open source industry standard HBase API, and has integrations with GraphDBs, TSDBs, Geospatial DBs ( link ). Actually, Bigtable was initially released in 2005, but wasn’t available to general public until 2015. Apache HBase was created based on Google’s publication Bigtable: A Distributed Storage System for Structured Data with initial release in 2008.
Bigtable has only one primary index known as rowkey which can look like ‘Field1#Field2#Field3’, if you decide to have multi-value rowkey. A rowkey should be designed with keeping future queries in mind. I’ll not go deep into things to keep in mind while designing the rowkey - you can find it here and designing rowkey for time series data.
There can be several instances where you need to modify your rowkey - first being load testing several rowkeys and figuring out the best one for you. Also, A table with particular rowkey can serve only one type of query better, you might want to store the same data with different rowkey for another type of queries to perform efficiently.
That being said, let’s see how we will achieve this -
- Exporting Bigtable data to GCS in Avro format by instantiating an open source Cloud Dataflow template (Bigtable-to-GCS-avro).
- Creating a empty table in Bigtable which will contain rows with updated rowkey (Alternatively, you can create the new table in a separate Bigtable cluster, if you don’t want it to affect your existing cluster).
- Importing Bigtable’s rows dump from GCS to new empty table after modifying the template code ( GCS to Bigtable template ) and launching it as Cloud Dataflow job.
The overall flow looks like this -
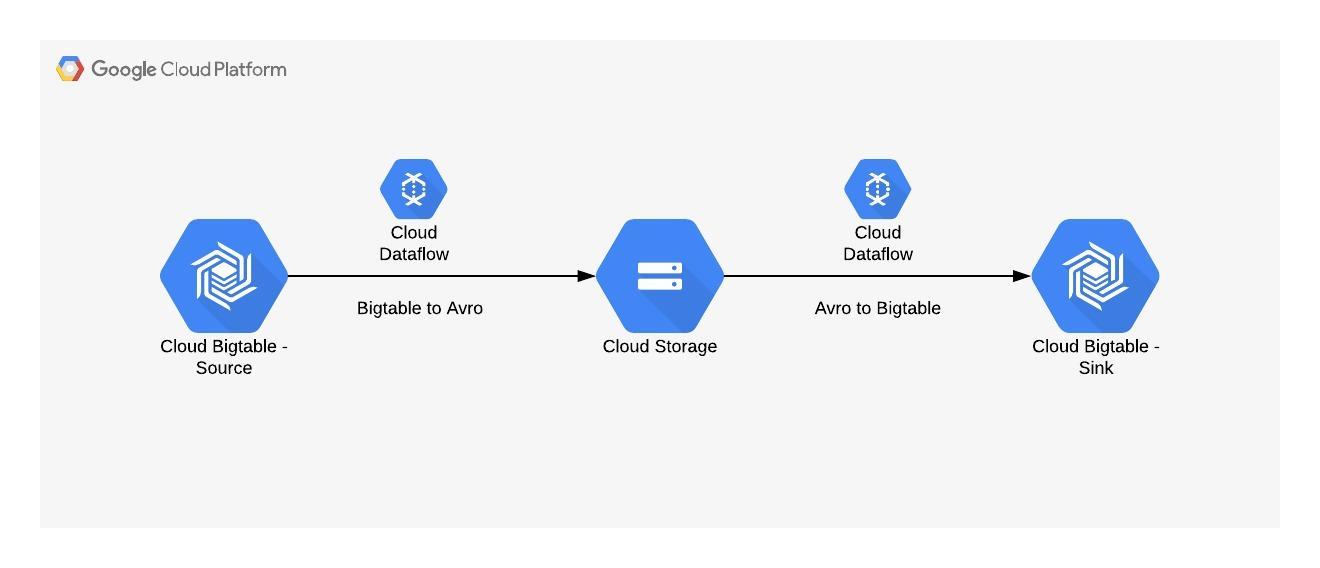
Let’s start -
Launch Dataflow export job from Bigtable to GCS in Avro -
We can launch the export job (Bigtable to GCS) directly from GCP console. Go to Big data -> Dataflow -> Create Job from template. You can fill out the details as shown below -
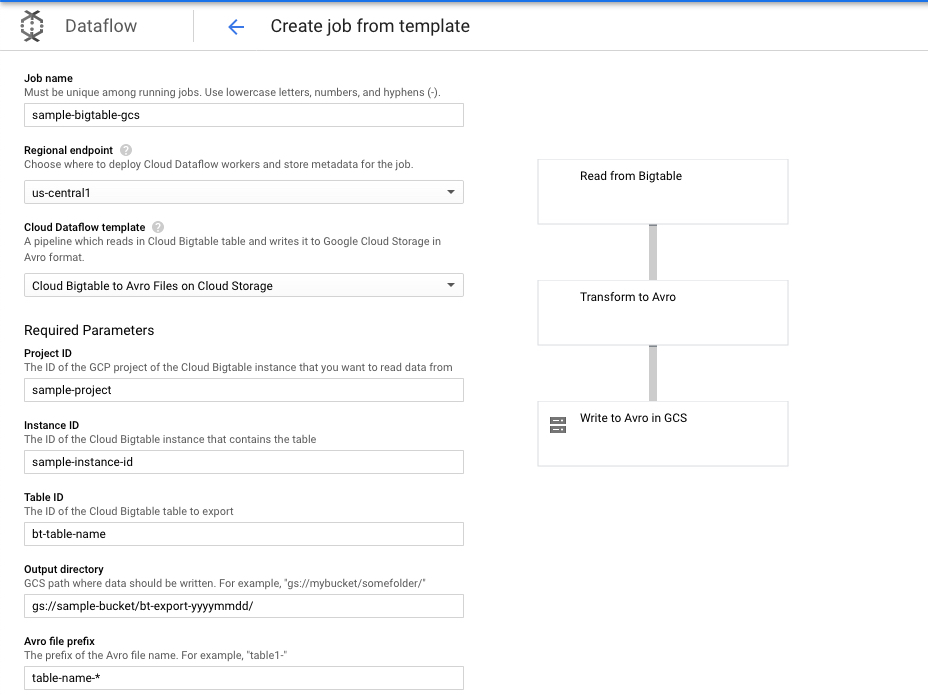
You can set the max-workers property to 10 and and instance type to n1-standard-4.
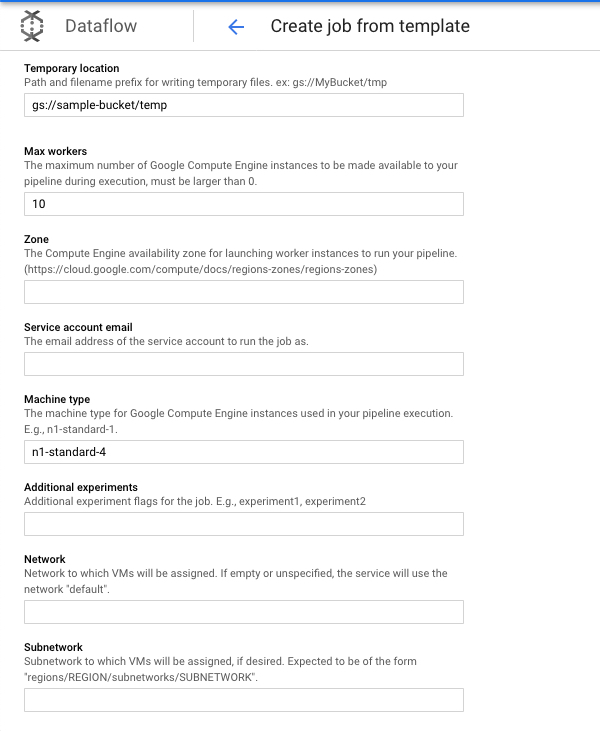
I recommend using minimum n1-standard-2 as I faced OutOfMemory errors while using n1-standard-1 workers in Dataflow job.
Also, number of vCPUs (workers * vCPU per machine) should be proportional to number of Bigtable nodes else it would lead to either over-utilization (Too many workers reading from small Bigtable cluster ) or under-utilization (small number of workers reading from relatively larger Bigtable cluster - resulting in more execution time).
For my use case, I had to take dump of 500GB table in Bigtable. I increased Bigtable cluster’s nodes to 12 and kept instance-type as n1-standard-4 and max-workers to 10. The export job took around ~45 mins.
Note : If you don’t set max-workers to any number. Dataflow can scale exponentially to 600 or 700 VMs based on size of your table. So, it’s good practice to have an upper bound on max VMs.
Launch the export job.
Create the sink table which will contain updated rowkey
First, make sure you have Google cloud SDK and cbt tool installed ( link ) or, for convinience, you can fire up a cloud shell in your project. cbt will be installed by default. We will store some default configuration in ~/.cbtrc file for cbt commands.
vim ~/.cbtrc
# enter following information
project = [YOUR_PROJECT_ID]
instance = [SINK_BIGTABLE_INSTANCE_NAME]
# save and exit
Now, we will list our source table’s column families because source table and our sink table should have same number and names of column families.
cbt --instance [SOURCE-TABLE-CLUSTER-ID] ls
This command will show the list of column family names and we will use the same CF names while creating the new table. Command for creating the new table is -
cbt createtable <table-id> families=[COLUMN_FAMILY_1]:maxversions=1,[COLUMN_FAMILY_2]:maxage=90d
This command creates a new table with 2 column families. In Bigtable, each cell (intersection of row and column) can have multiple versions along with the timestamp. So, in the above command, I have set the garbage collection policy on CF1 to retain only the latest version and the cells under CF2 will expire after 90 days (90 days after they were created). Please note that mentioning garbage collection policy is optional. By default, bigtable will store all versions of the cell value indefinitely. You can refer to the docs for command here.
Importing from GCS to Bigtable with updated rowkey
We will be using this Dataflow template but we will not be launching directly from GCP console. The provided template job reads from GCS (the export we took in 1st step) and writes to the sink table as it is without any transformation. We need to add one transformation which is modifying the rowkey.
You can clone this Github repository to your local machine. Navigate to class - DataflowTemplates/blob/master/src/main/java/com/google/cloud/teleport/bigtable/AvroToBigtable.java and modify the class AvroToBigtableFn. I have shown an instance of the modified method. Basically, the flow is to read the original rowkey, split it by the delimiter (the character ‘#’ will be the delimiter in most of the cases), re-arrange the fields and store it as another string.
static class AvroToBigtableFn
extends SimpleFunction<BigtableRow, KV<ByteString, Iterable<Mutation>>> {
@Override
public KV<ByteString, Iterable<Mutation>> apply(BigtableRow row) {
String ini_rowkey = StandardCharsets.UTF_8.decode(row.getKey()).toString(); // readig original rowkey
String finalKey = "";
String[] keyString = ini_rowkey.split("#");
try {
finalKey = finalKey + keyString[2] + "#" + keyString[1] + "#" + keyString[3] + "#" + keyString[0];
}
catch(Exception e) // if the rowkey doesn't contain all the assumed fields
{
e.printStackTrace();
finalKey=ini_rowkey; // I am keeping it as initial rowkey, but you can ignore as well or push this bad data point to another branch for later analysis
}
// everything in bigtable is stored as bytes
ByteBuffer b = ByteBuffer.wrap(finalKey.getBytes());
ByteString key = ByteString.copyFrom(b);
// ByteString key = toByteString(row.getKey());
// BulkMutation doesn't split rows. Currently, if a single row contains more than 100,000
// mutations, the service will fail the request.
ImmutableList.Builder<Mutation> mutations = ImmutableList.builder();
for (BigtableCell cell : row.getCells()) {
SetCell setCell =
SetCell.newBuilder()
.setFamilyName(cell.getFamily().toString())
.setColumnQualifier(toByteString(cell.getQualifier()))
.setTimestampMicros(cell.getTimestamp())
.setValue(toByteString(cell.getValue()))
.build();
mutations.add(Mutation.newBuilder().setSetCell(setCell).build());
}
return KV.of(key, mutations.build());
}
}
You can build and create the template and store it in GCS as shown in this readme file but don’t execute the template. We will do the same through the console.
Go to Dataflow ‘create job from template’ page in console.
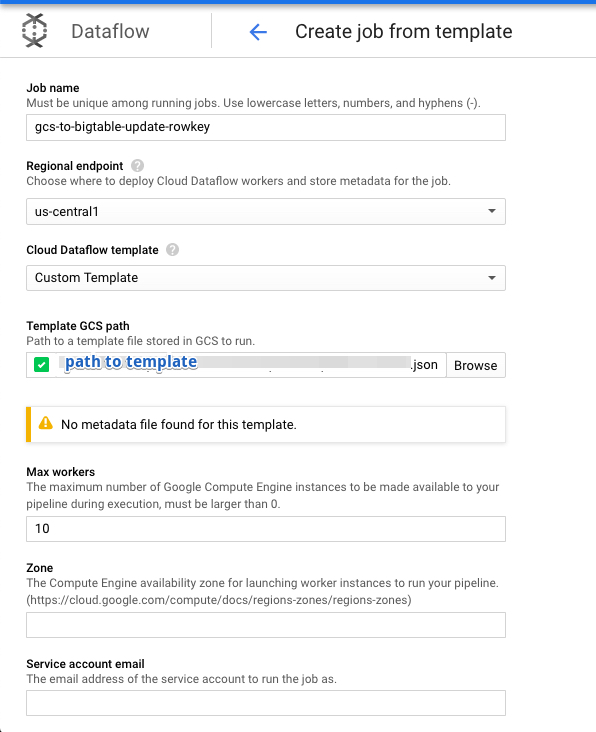

we need to define additional parameters as well. Every parameter pertains to sink bigtable instance and table name (the new bigtable we created in step 2 above). _inputFilePattern i_s the path to the dump files in GCS we took in step1. Remember to use asterisk to select multiple avro files.
Also, you might want to increase the nodes in your bigtable cluster to around ~10-12 to support this heavy write job because the Dataflow might be writing close to 1 mil rows per sec.
Go ahead and launch the import job.
Thanks to Akash for helping me with this solution.

